| Version | Date | Notes | By |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 2020-12-02 | Initial release | ROB |
| 1.1 | 2023-06-19 | Small note on frontend script execution | ROB |
| 1.2 | 2023-06-20 | Altered attribute reference from dynamic attributes to data types | ROB |
Introduction
The WeFlow scripting engine is a flow based programming language developed specifically for "Programming in the small" inside a bpmn process engine (handling the logic that decides which flows a gateway selects or how to handle the information sent by a webservice).
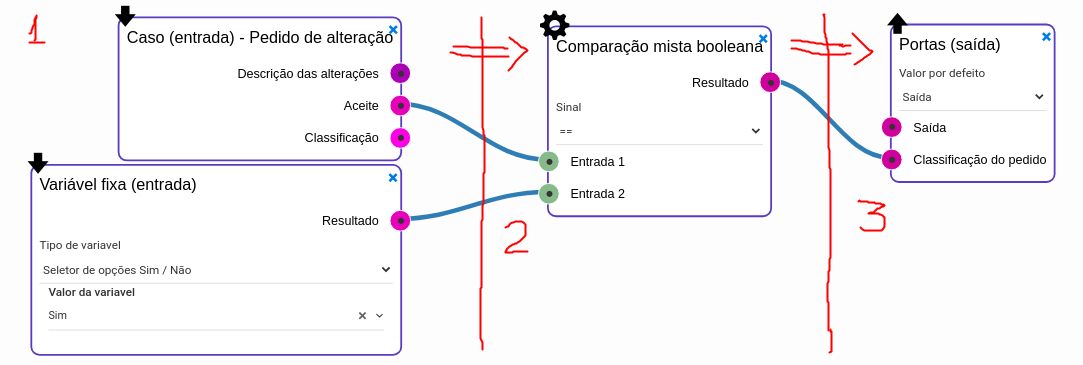
A WeFlow script is composed of one or more entry components, any number of processing components, and one or more exit components. Each component is concerned only with a very specific task (for example read case variable, write case variable, calculate sum of two attributes, etc...).
Each WeFlow component has any number of input sockets, output sockets and options.
The sockets can connect to a socket of the same type, with a few exceptions, that will be detailed further ahead.
The execution of a WeFlow script is linear (each component waits for all previous components to execute).
Components
WeFlow has 3 major types of components, start, processing end end components. When a WeFlow script starts execution it will seek out start components and start processing from there (A WeFlow script without start components will never do anything).
The start components will output a value per output socket they have and it is up to the next components to retrieve the values through the connected sockets. For many components it is not required to have all sockets connected (many sockets are optional).
The exit components may change based on the context of the WeFlow script (for example if the script is created for a gateway, the exit will be an exit flow selector).
Sockets
The sockets define a single attribute, variable, webservice variable / attribute or flow (more on flows later). It informs the user / script of what values a component inputs / outputs and also which sockets can connect to which.
Socket types
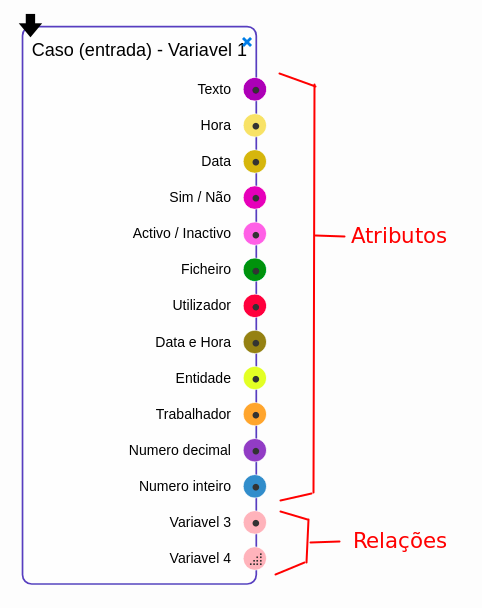
Attribute - This socket type passes through a single value (as defined in the process / variable definitions / data type for each attribute; depending on the multiplicity of the data type, the value may be a single value or an array of multiple values). Note, inside the scripting engine the values for attributes like "User selector" are passed through by id.
Variable - This socket passes through an entire case variable with all attributes attached.
Flow - This is a special system that indicates that operations between unfolding and folding operations are executed per member of flow array (more explanations in the flow section of this document).
Socket multiplicity
As mentioned abobe, sockets can refer to a string or a number or an user, or an array of strings, numbers or users. this is denoted in the WeFlow script designer by diferent symbols inside the socket.

Flow
This system is still in development, more "flowable" components are required, a filtering system is required and diferent relation write modalities (other than overwrite) are required.
The flow system is used to unfold a variable socket with multiple variables, execute operations per variable (instead of on the array) and refold the variables back into the array.
Frontend
The frontend editor for the WeFlow scripting system uses a library called rete.js to provide the editing environment (component and socket drawing and interactions). The library reduces the drawing of the script down into a json, which is then validated by the backend for required options and socket connections.
Frontend scripting
It is now possible for WeFlow™ scripts to be executed in the frontend with a limited set of components (case inputs / outputs, logic and arithmetic for now, more components may be added in the future). The result of these scripts allow values to be altered in real time or manipulation of form components (for now it manipulates visibility, disabled status (non interactive but visible) and required (form has star next to name or not)).
More form component manipulation may be added in the future.